Itroduction :

Which is often referred to as the Golden age of the rear-engine car. The automotive industry witnessed a remarkable transformation in design and engineering during the mid-20th century. This period, primarily spanning from the 1950s to the 1970s, was characterized by a surge in the popularity of rear-engine configurations in a variety of vehicles, most notably in small cars, sports cars, and even mass-market models. The rear-engine layout allowed for a unique driving experience, improved traction, and innovative design, making significant contributions to automotive culture and engineering. The Golden Age of the Rear-Engined Car.
The influence and legacy of rear-engined cars are still felt today, though their prevalence has diminished in favor of front and mid-engine designs due to changing consumer preferences and technological advancements. This article seeks to delve into the history of rear-engined vehicles during their peak popularity, explore the iconic models that defined the era, discuss the unique advantages and challenges these cars presented, and examine their lasting impact on automotive design.
A Brief History of The Golden Age of the Rear-Engine Car:
The concept of The Golden Age of the the rear-engine car is not a recent innovation; it dates back to the early days of motoring. Notably, the Tatra V570, created by Czech engineer Hans Ledwinka in the 1930s, is often recognized as one of the earliest examples of a mass-produced rear-engine vehicle. However, it was not until the post-World War II era that rear-engined layouts became widely adopted.
The impetus for this shift stemmed from the need for affordable and practical vehicles during the post-war economic boom. Manufacturers sought designs that offered space-efficient interiors, lower production costs, and enhanced drivability. The Volkswagen Beetle, introduced in 1938, played a significant role in popularizing the rear-engine format. Under the direction of Ferdinand Porsche, the Beetle combined simplicity with functionality, utilizing a rear-mounted, air-cooled flat-four engine. By the 1950s and 1960s, the Beetle had surged in popularity, becoming a symbol of the era and a significant competitor to more traditional front-engine cars.
The Rise of Iconic Rear-Engined Models :
As the rear-engine layout gained traction, several iconic models emerged from various manufacturers, each contributing to the legacy of rear-engined cars in unique ways.
1. Volkswagen Beetle :

Undoubtedly the most famous rear-engine car, the Volkswagen Beetle achieved international acclaim for its reliable performance, affordability, and distinctive design. Produced in large numbers, it captured the hearts of consumers worldwide and solidified its place in automotive history. With a production run extending from 1938 to 2003, the Beetle remains one of the best-selling cars of all time, with over 21 million units produced.
2. Porsche 911 :
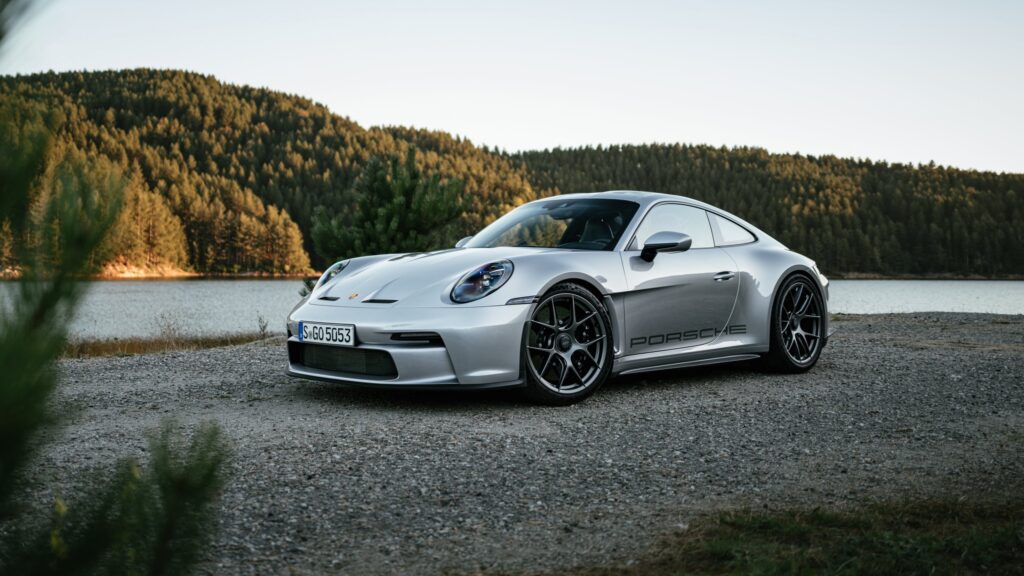

The Porsche 911, introduced in 1964, represents the pinnacle of rear-engine sports cars. Featuring a distinctive blend of performance and practicality, the 911 quickly became a household name among car enthusiasts. Its rear-engine configuration contributed to its exceptional handling and stability, allowing it to thrive on both the road and the racetrack. The 911 has undergone numerous generations of refinement but has remained true to its iconic rear-engine layout.
3. Chevrolet Corvair :
The Chevrolet Corvair, launched in 1959, was an American response to the Volkswagen Beetle. It featured a rear-mounted, air-cooled flat-six engine and was marketed as a compact and innovative vehicle. Despite its initial popularity, the Corvair’s reputation suffered due to safety concerns raised by consumer advocate Ralph Nader, particularly regarding handling characteristics that led to oversteer.
4. Renault 4CV :

Launched in 1947, the Renault 4CV was one of France’s first mass-market cars and featured a rear-engine layout that maximized interior space while minimizing production costs. The 4CV became a symbol of post-war recovery and was embraced for its practicality and affordability, selling over a million units before production ceased in 1961.
5. Fiat 500 :
Competing directly with the Beetle, the Fiat 500 made its debut in 1957 and quickly became synonymous with Italian urban mobility. Its compact design, rear-engine layout, and charming aesthetics made it an instant classic, with approximately four million units sold over its production lifespan. The 500’s enduring appeal is seen in its modern iterations, which retain the iconic styling while embracing contemporary automotive technology.
6. The Hillman Imp :
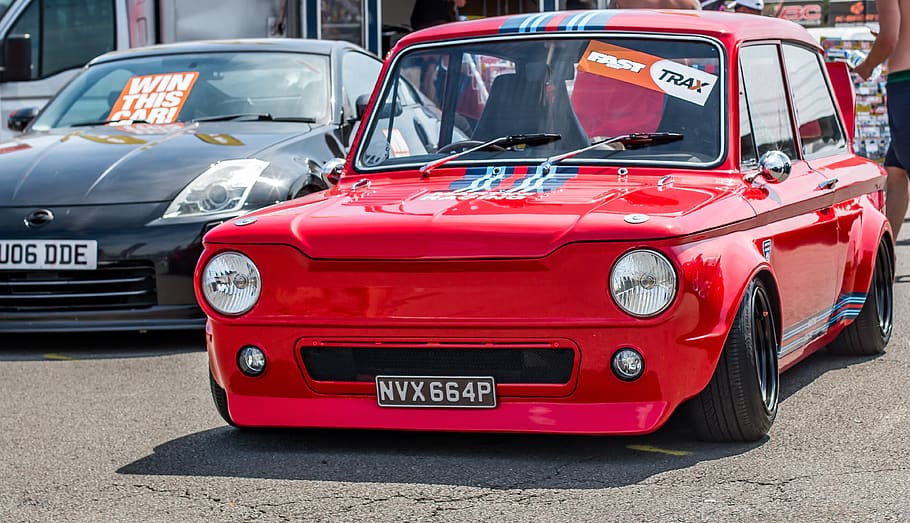

The Hillman Imp, produced from 1963 to 1976, aimed to challenge the dominance of the Mini with its rear-engine layout and lightweight design. The Imp offered sporty performance and practicality, although it struggled with reliability issues that impacted its reputation. However, it carved a niche as a beloved classic for enthusiasts seeking a unique take on small-car design.
Advantages of Rear-Engine Configuration :

The rear-engine layout offers several notable benefits that contributed to its appeal during the golden age of rear-engined cars. Understanding these advantages highlights why manufacturers leaned towards this design during that time.
1. Improved Traction and Handling :
One of the key advantages of a rear-engine layout is enhanced traction. With the engine’s weight positioned over the rear wheels, vehicles are better equipped to handle acceleration, particularly in challenging weather conditions. This configuration also improves weight distribution, resulting in enhanced stability and control during cornering, making rear-engined cars popular in motorsports.
2. Space Efficiency :
The rear-engine design allows for greater interior space. By eliminating the need for a large front engine compartment, manufacturers could design more compact vehicles with usable interior cabin space. This was especially important for small cars targeting a broader customer base, as it provided increased comfort without sacrificing maneuverability.
3. Streamlined Design :
Aerodynamics played a significant role in the adoption of rear-engined configurations. The layout permits smoother lines and shapes, reducing air resistance and improving fuel efficiency. This was particularly advantageous for smaller vehicles, where the engine’s placement did not compromise seating or cargo space.
Challenges Faced by Rear-Engined Cars:
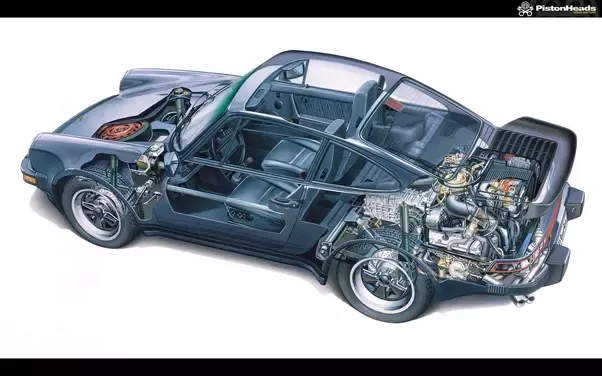
Despite their numerous advantages, rear-engined cars were not without their challenges. These issues contributed to their decline in popularity as consumer preferences evolved.
1. Oversteer Sensitivity :
While the rear-engine layout offers improved traction, it can also lead to oversteer, which occurs when the rear wheels lose grip before the front wheels during a turn. This can make rear-engined cars more challenging to handle for inexperienced drivers, leading to safety concerns that impacted consumer confidence (cati, 2020).
2. Cooling Difficulties :
The placement of the engine at the rear can complicate the cooling process, particularly for air-cooled engines. The proximity to the rear compartment can make it more challenging to manage engine temperatures effectively, leading some manufacturers to struggle with overheating issues in certain models.
3. Limited Market Appeal :
As consumer preferences shifted toward front-wheel drive (FWD) and mid-engine layouts, the market for rear-engined cars gradually diminished. The rise of the BMC Mini, which helped catalyze the popularity of FWD configurations, played a significant role in reducing the presence of rear-driven vehicles (John Simister, 2017).
The Cultural Impact of Rear-Engined Cars :
The golden age of rear-engined cars extends beyond just engineering and performance; these vehicles made significant contributions to popular culture during their time.
1. Motoring Icons and Cultural Symbols :
Rear-engined vehicles like the Volkswagen Beetle and Porsche 911 became cultural symbols that transcended automotive enthusiasts. The Beetle, for example, became synonymous with counterculture movements and was celebrated in music and film, most notably in the movie “The Love Bug.” The 911, on the other hand, was often showcased in racing films and remains a status symbol among sports car enthusiasts.
2. Automotive Innovations :
The era of rear-engined cars witnessed several engineering innovations that have shaped subsequent automotive design. From advancements in aerodynamics and weight distribution to the refinement of small-displacement engines, many modern vehicles owe their effectiveness to the lessons learned during the heyday of rear-engine configurations.
3. Nostalgia and Collectibility :
As time has passed, the allure of rear-engined cars has experienced a revival among classic car enthusiasts. Many of these vehicles have become highly sought after in collector circles, with enthusiasts investing time and resources into restoring and preserving these iconic models. The nostalgia attached to these designs continues to drive interest in classic car shows and exhibitions today (John Simister, 2017).
The Decline of Rear-Engined Cars :
Despite their popularity, the golden age of rear-engined cars eventually waned in the late 1970s. Several factors contributed to this decline:
1. Shift in Consumer Preferences :
As automobile technology evolved, consumers began to prioritize safety, practicality, and performance in their vehicle choices. The rise of front-wheel drive and mid-engine layouts provided manufacturers with new opportunities to create more versatile and safe vehicles that appealed to a broader market demographic (Abeer Mohamed, 2024).
2. Technological Advances :
Advancements in automobile manufacturing and design practices allowed for new configurations that improved performance while addressing some of the challenges associated with rear-engine designs. This shift led to a gradual phase-out of rear-engine models as manufacturers adapted to changing market dynamics and consumer preferences (Abeer Mohamed, 2024).
3. The Rise of Luxury and Performance Brands :
Brands focused on comfort, luxury, and mid-engine performance cars grew in prominence, further diminishing the market presence of rear-engine designs. Manufacturers such as Porsche and Ferrari leveraged their expertise in engineering to craft luxury sports cars that appealed to a different segment of automotive consumers.
FAQs:
1. What are the most iconic rear-engine cars?
The most iconic rear-engine cars include the Volkswagen Beetle, Porsche 911, Chevrolet Corvair, Renault 4CV, and the Fiat 500. These models are recognized for their innovative design, performance, and cultural significance.
2. Why did rear-engine cars become less popular?
Rear-engine cars became less popular due to shifting consumer preferences towards front-wheel drive and mid-engine configurations. Safety concerns, oversteer handling characteristics, and evolving market demands also contributed to their decline.
3. What advantages do rear-engine cars offer?
Rear-engine cars offer advantages such as improved traction, increased interior space, and streamlined design, which contributes to better aerodynamics. They are often more stable under acceleration and suitable for specific driving conditions.
4. Are rear-engine sports cars still being produced?
While the rear-engine configuration isn’t as common as it once was, some manufacturers, like Porsche with the 911, continue to produce rear-engine sports cars. Additionally, niche manufacturers occasionally explore rear-engine designs for unique models.
5. Can rear-engine cars be safe?
Yes, rear-engine cars can be safe with modern engineering advancements and safety features. However, early models faced challenges in handling and stability, which have been addressed in newer rear-engine designs through enhancements in suspension and chassis dynamics.
Conclusion:

The golden age of the rear-engine car represents a significant chapter in automotive history, characterized by innovative engineering and cultural impact. Despite their decline in popularity, the legacy of rear-engine vehicles endures, with many enthusiasts and collectors revitalizing interest through restoration projects and celebrations of classic automotive culture. As the industry continues to evolve, the lessons learned from the golden age of rear-engine cars will undoubtedly inform future designs and innovations, ensuring that this remarkable era remains a vital part of automotive discourse for generations to come.